Learning about logistics may help you better understand the various operations involved in the process and determine how to enhance them. But how do you enter into the realm of outbound logistics? You need proper management and planning to move products from their origin to their final destination.
This blog will explore the definition of outbound logistics, its activities, benefits, and the comparison between inbound vs outbound logistics.
Key Takeaways:
Here are some important reminders you may consider when improving your outbound logistics operations:
- Utilizing a Warehouse Management System (WMS) to streamline the packing and shipping process is a better idea.
- Implement a Transportation Management System (TMS) to reduce transportation costs and provide timely shipment tracking drastically.
- Leverage crowdsourced delivery to provide a quick and efficient solution for escalating customer experience.
- Invest in direct-to-consumer sales to own the customer relationship and collect valuable data.
- Ensure top-tier customer satisfaction by providing cost-free shipping, convenient options, and real-time tracking visibility.
Outbound Logistics Definition
The definition of outbound logistics refers to the process of transferring finished inventory from a supply chain management, including retrieving it from storage areas, satisfying customer orders, and finally delivering them to end customers.
Any process about order processing confirmation, from picking and packing through outbound shipping, last-mile delivery, customer service, and troubleshooting, is classified as an outbound logistics process. You’ll need to monitor critical performance indicators (or KPIs) to ensure that your inbound and outbound logistics procedures are running well.
- Order volume: The total number of orders received and fulfilled by your business.
- Perfect order rate: The rate at which orders are accurately fulfilled in full and on time.
- Shipping lead time: The amount of time it takes for a shipment to reach
- Order fill rate: The percentage of orders placed that are completed accurately and on time.
- Customers expect a timely response: Fast customer service is paramount for meeting their expectations.
- Supply chain costs: The total costs associated with managing your supply chain.
- Average delivery time: Average time of the delivery process.
Difference Between Inbound and Outbound Logistics
Both involve efficiently transporting products or items from one point to another, optimizing each supply chain’s distribution center – outbound network. However, they still have differences in terms of the following:

Definition and direction
Inbound logistics involves bringing merchandise to a business, while outward-bound logistics is the movement of goods or services from a company to its customer.
Primary role
Inbound logistics serves an essential purpose – accepting goods from vendors for the company. Simultaneously, outbound logistics is in charge of delivering these products to customers promptly and efficiently.
Key relationships
Building professional partnerships with wholesalers, retailers, distributors, and customers is key to successful outward-bound logistics. On the other hand, businesses can foster meaningful relationships with distributors, vendors, and suppliers to optimize their inbound logistics.
Processes
Inbound logistics involves the acquisition of goods, materials handling, and warehousing storage. On the other hand, outward-bound logistics include inventory control, transportation, and order fulfillment.
Focus
Inbound logistics typically pay attention to the supply side of things, while outward-bound logistics are intent on meeting customer demand.
Strategy
Inbound logistics necessitate procuring all components necessary to assemble a final product, while outward-bound strategies focus on supporting sales and meeting customer demands as an income generator.

Outbound Logistics Activities
Warehouse management systems (WMS), inventory control, and order fulfillment are some of the activities involved in outbound logistics. Here’s an overview of the process.
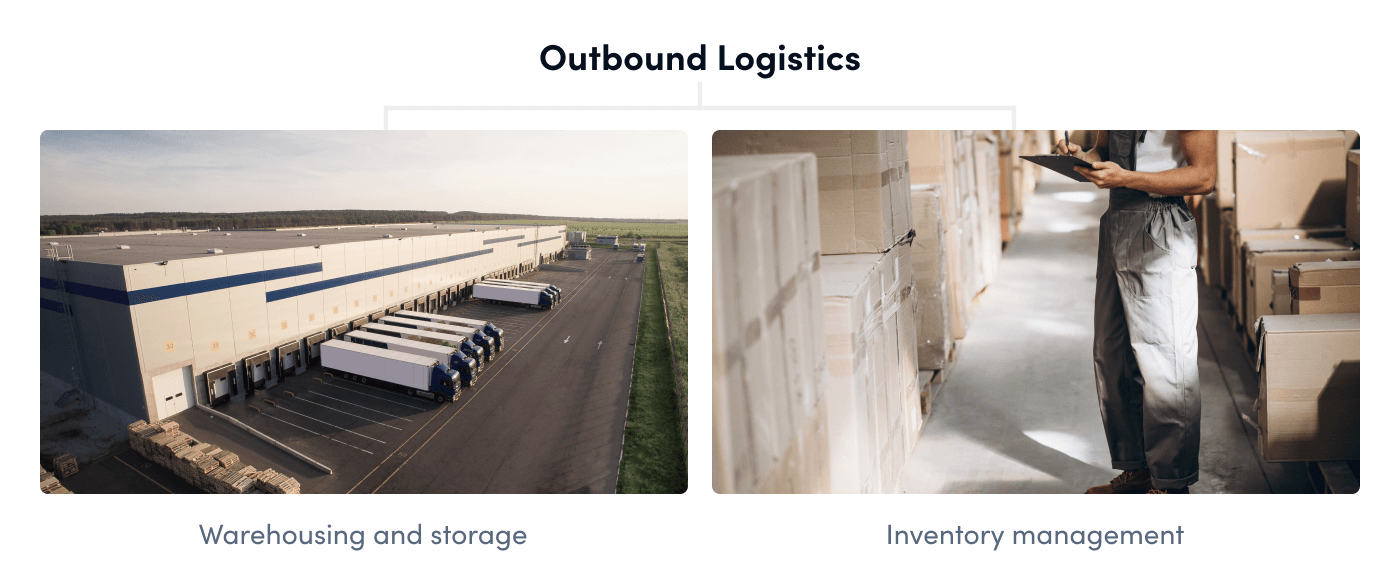
Warehouse and storage management
Outbound logistics operations guarantee that products are appropriately maintained and stored in the appropriate conditions while organizing them to their destination.
Inventory management
Inventory management objectives include preserving inventory and order accuracy and product quality by preventing damage, theft, obsolescence, or spoiling.
Transportation
Depending on the product type, there are various options for outbound shipping. For instance, large items such as heavy machinery can be shipped in small order amounts via truck. At the same time, perishable goods like fresh flowers may need to be distributed by air in refrigerated containers.
Delivery
On-time delivery is key to success. Moreover, the customer’s order must include the correct items and amounts, and the shipment can’t get lost or damaged in transit. Outbound logistics is in charge of this stage.
Distribution Channels
Products must be delivered to the right destination, which sometimes means a distributor or a third-party logistics provider. Outbound logistics activities work to establish partnerships with these entities and ensure that the goods are delivered on time.
Last-mile Delivery
The last mile is typically the most expensive and inefficient element of the delivery process. The term derives from the early days of telephone service when connecting households to the mainline were time-consuming and costly. Last-mile logistics services include home grocery delivery from a nearby store and package delivery by a common carrier.
Delivery Optimization
Optimizing delivery includes decreasing costs and satisfying ever-increasing consumer expectations for speed and visibility. These two things frequently go hand in hand.
7 Steps of The Outbound Logistics Process
The following are the typical outbound logistics processes that companies use to get their products and services to their customers:
1. Order Placing
Allowing your customers to purchase from your online store easily is simple. After browsing and selecting the product of their choice, they can then proceed through the ordering process.
2. Confirmation and Picking
Once the order is confirmed and the payment is processed, the warehouse will send the order. The warehouse workers will then find the relevant product and place it aside, ready to be packed.
3. Packing
When the product or products have been picked, they will be packaged and prepared for outbound shipping. This would typically involve moving the products to the loading dock.
4. Pick Up
Subsequently, the products will be collected and transported via freighter trucks. This step will typically involve several orders being picked up so that space and time are maximized for efficiency.
5. Transportation to Distribution Centers
The freight trucks will transport the packed goods to a distribution center. After their arrival, the goods will be unpacked and prepared for dispatching via multiple distribution channels.
6. Package Pick Up
Smaller delivery trucks will pick up individual orders for their specified delivery area at the distribution center.
7. Final Delivery
The delivery trucks or vans will then deliver the package to the final destination per the initial order. This brings the outbound process to an end.

Benefits of Outbound Logistics

Customer expectations for delivery have become increasingly higher, and outbound logistics can help to meet those expectations. Specifically, here are some of the benefits:
- Fast deliveries
- Order cancellations decreased
- On-time deliveries increased
- Fewer delivery issues or errors
- Less damage and loss in transit
- Reduced expenses for your company and the customer
- Decreased returns
- Higher customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Stronger company reputation
- Better business planning
Challenges of Outbound Logistics

Take a look at these widespread issues individuals come across when managing this procedure:
- The complexity of customer orders takes a lot of work to manage.
- Identifying the most efficient shipping routes.
- Meeting delivery deadlines.
- Following outbound shipping restrictions.
- Working with operations, suppliers, and carriers to coordinate.
- Returns and reverse logistics management
- Making sure that products are delivered on time and in good shape.
- Transportation costs.
- Increasing customer expectations
- Packaging products
How to Overcome Outbound Logistics Challenges

Fortunately, there are solutions to these difficulties. Consider incorporating some of these tactics:
- Use intelligent route planning and route planning tools to optimize delivery routes.
- Determine when quick delivery starts and arrange your operations accordingly.
- Adapt to the existing inventory tactics that are being employed with your business strategy.
- Collaborate with a third-party logistics company to handle your outbound logistics.
- To streamline order picking, packaging, and shipping operations, utilize a warehouse management system (WMS) like SkuVault.
- Collaborate with a logistics partner who is willing to help you.
- Enhance communication among operations, suppliers, carriers, and customers.
- Using Returns Management Software, you better manage returns and reverse logistics.
- Provide customer service that exceeds expectations.
- Harness the power of Transportation Management Software to reduce transportation costs and streamline shipment tracks drastically.
- Streamline your packing and shipping process by linking your Warehouse Management System with the applicable carrier system.
Trends in Outbound Logistics
These days, outbound logistics is becoming more and more automated. Here are some of the trends you should understand:
- Increased need for visibility
Utilizing traditional logistics management systems to monitor and maintain control of your freight services is a taxing task, even when you know the truck’s location or orders. However, managing multiple delivery providers without such visibility is an insurmountable challenge.
- Crowdsourced Delivery
Crowdsourced delivery offers an expeditious answer to advancing the customer experience while providing invaluable aid to a beleaguered distribution system. It enables companies to quickly and efficiently ship items while also ensuring traceability.
- Direct-to-Consumer Sales
As more brands move to sell their consumer products directly, they are motivated by the potential for increased customer relationships and data collection. By selling through eCommerce platforms, distributors, or retail chains, companies can own the customer relationship while leveraging valuable insights from customers’ data.
4. The customer experiences
Of all the aspects of outbound logistics, it is the last mile that holds sway over customer satisfaction. Nowadays, customers are looking for quick, cost-free shipping with convenient options. In addition, an overwhelming majority of modern consumers insist on real-time tracking visibility – leaving no room for error!

Optimize Your Outbound Logistics Operations with Hopewell Logistics
Efficient third-party Logistics operations are the key to success for any business. To ensure your outbound logistics operations are up-to-date, consider partnering with Hopewell Logistics Transportation Management Service.
Whether a huge retailer or an SME wants to hand over your e-commerce fulfillment, our comprehensive logistics solutions can help create a flawless buying experience for all your customers. Our services are unmatched in top-tier customer satisfaction – take advantage today!
Take Advantage of This Outbound Logistics Guide to Boost Your Business Revenue!
Outbound Logistics is essential to any business that relies on shipping goods and understanding its core components can help you craft a successful strategy. Collaborating with a third-party logistics company, employing a warehouse management system, and utilizing returns management software are necessary to ensure efficient and effective outbound logistics operations.






